Chapter 26 Introduction to Git
26.1 Introduction
26.1.1 Useful shell commands
See location / working directory:
pwdSee what is in current directory:
ls(list files)Changing directory:
cd file_placeEditing a file:
nano file_nameDelete, add, change contents of a file
Save changes:
Ctrl + OExit the text editor:
Ctrl + X
Create or edit a file:
echoCreate a new file
echo "Review for duplicate records" > todo.txtAdd content to existing file
echo "Review for duplicate records" >> todo.txt
Checking Git version:
git --version
26.2 Making changes
26.2.1 Storing data with Git
The commit structure
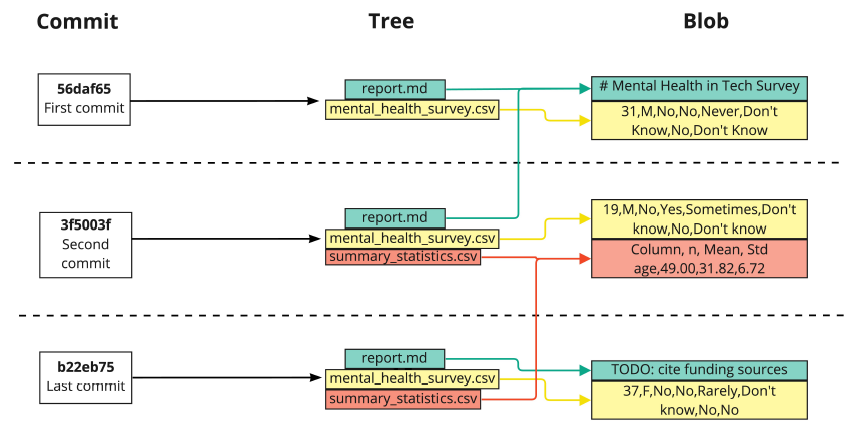
Git commits have three parts:
Commit
contains the metadata
Git hash
allow data sharing between repos
If two files are the same, then their hashes are the same
eg., the last summary_statistics.csv hash is 3f5003f
Tree
- tracks the names and locations in the repo
Blob
binary large object
may contain data of any kind
compressed snapshot of a file’s contents
Viewing a repository’s history
git log
Show more recent commits: press space
Quit the log and return to the terminal: press q
Finding a particular commit
git show c27fa856
Only need the first 6-8 characters of the
hashUseful for viewing changes made in a particular commit
(vs
git diffcompare changes between commits)
26.2.2 Viewing changes
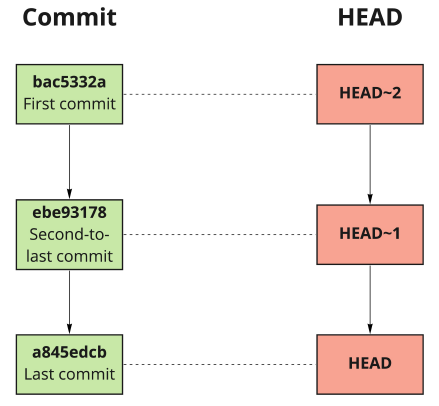
The HEAD shortcut
Compares staged files to the version in the last commit
Use a tilde
~to pick a specific commit to compare versions
Changes per document by line
git annotate file_name
Summary
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
git show HEAD~1 |
Show what changed in the second most recent commit |
git diff 35f4b4d 186398f |
Show changes between two commits |
git diff HEAD~1 HEAD~2 |
Show changes between two commits |
git annotate file |
Show line-by-line changes and associated metadata |
26.2.3 Undoing changes before committing
Staged files
Unstaging a single file
git reset HEAD file_name
Unstaging all files
git reset HEAD
Unstaged files
Undo changes to an unstaged file
git checkout -- file_namecheckoutmeans switching to a different version, defaults to the last commitlosing all changes made to the unstaged file forever
Undo changes to all unstaged files
git checkout .- This command must be run in the main directory
26.2.4 Restoring and reverting
Customizing the log output
By restrict the number with -
git log -3
- shows the three most recent commits
git log -3 file_name
- shows the three most recent commits of one file
By restrict with date
git log --since='Apr 2 2022'
- since particular date
git log --since='Apr 2 2022' --until='Apr 11 2022
- between two dates
Cleaning a repository
See what files are not being tracked
git clean -n
Delete those files
git clean -f
26.3 Git workflows
26.3.1 Configuring Git
Levels of settings
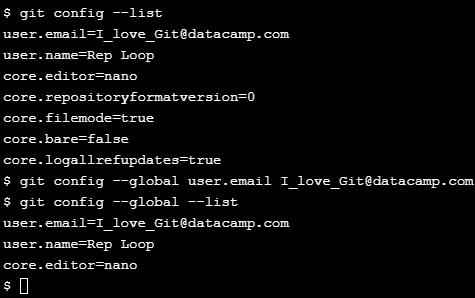
git config --list: view the list of all customizable settingsGit has three levels of settings:
1.
--local: settings for one specific project2.
--global: settings for all of our projects3.
--system: settings for every users on this computer
Changing our settings
git config --global setting value
Change email address to johnsmith@datacamp.com:
git config --global user.email johnsmith@datacamp.comChange username to John Smith:
git config --global user.name 'John Smith'
Creating a custom alias
Set up an alias through global settings
Typically used to shorten a command
eg., To create an alias for committing files by executing
ci:git config --global alias.ci 'commit -m'We can now commit files by executing:
git ciTracking aliases:
git config --global --list
Ignoring specific files
nano .gitignore
26.3.2 Branches
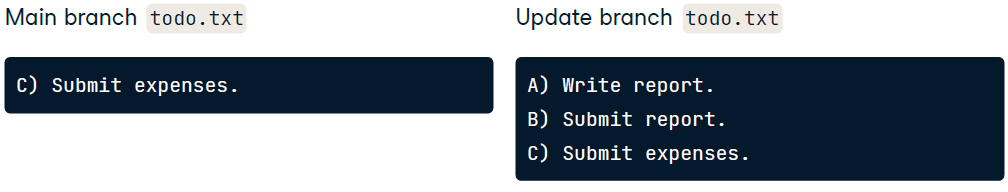
There’re 3 branches, 2 merges in the picture.
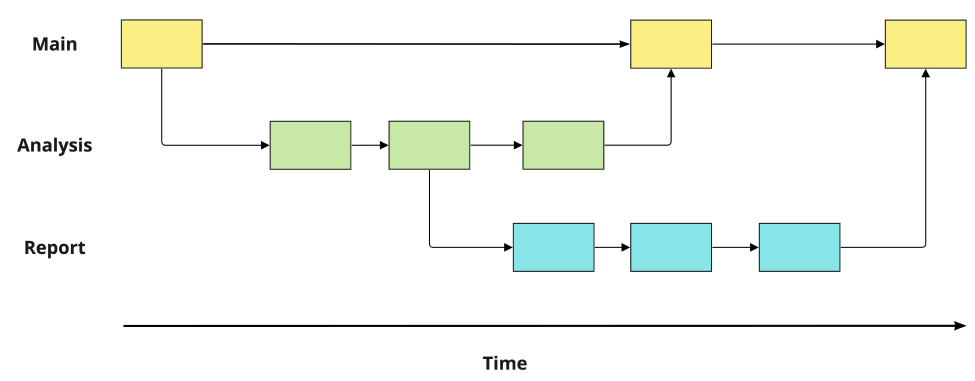
Source and destination
When merging two branches:
the commits are called parent commits
source: the branch we want to merge fromdestination: the branch we want to merge intoeg., When merging
AnalysisintoMain,Analysis=sourceMain=destination
Identifying branches
git branch
*= current branch
Creating a new branch
git checkout -b branch_name
The difference between branches
git diff branch_1 branch_2
26.3.3 Working with branches
Switch branches
git checkout branch_name
Why do we merge branches?
main= ground truthEach branch should be for a specific task
Once the task is complete we should merge our changes into
main- to keep it up to date and accurate
Merging branches
git merge source destination
eg., To merge
summary-statisticsintomaingit merge summary-statistics main
26.4 Collaborating with Git
26.4.1 Creating repos
Benefits of repos
Systematically track versions
Collaborate with colleagues
Git stores everything!
Don’t create a nested repos
Creating a new repo
git init repo_name
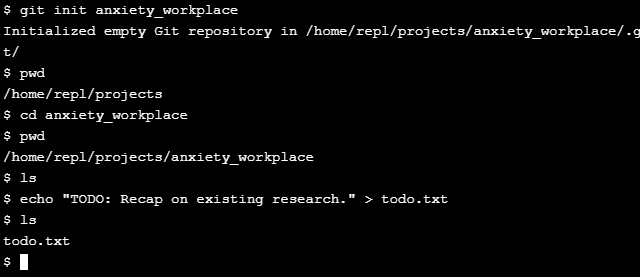
Converting a project
git init
26.4.2 Working with remotes
Benefits of remote repos
Everything is backed up
Collaboration, regardless of location
git cloneis a very useful command for copying other repos onto your local computer, whether from another local directory or remote storage such as GitHub.
Cloning locally
git clone path-to-project-directory
git clone /home/john/repogit clone /home/john/repo new_repo_name
Cloning a remote
Remote repos are stored in an online hosting service e.g., GitHub, Bitbucket, or Gitlab
We can clone a remote repo on to our local computer
git clone [URL]ed.,
git clone https://github.com/datacamp/project
Identifying a remote
git remote
Git stores a remote tag in the new repo’s configuration
Getting more information
git remote -v
Creating a remote
git remote add name URL
Defining remote names is useful for merging branches
git remote add george https://github.com/george_datacamp/repo
26.4.3 Pulling from a remote
Two ways to Synchronize local and remote repos
fetchandmergeFetching from a remote
git fetch remote_name local_branchSynchronizing content
git merge remote_name local_branch
pullShort cut of above 2 steps process
git pull remote_name local_branch
Important to save locally before pulling from a remote
26.4.4 Pushing to a remote
git push
Save changes locally first
Push into
remote_namefromlocal_branchgit push remote_name local_branch
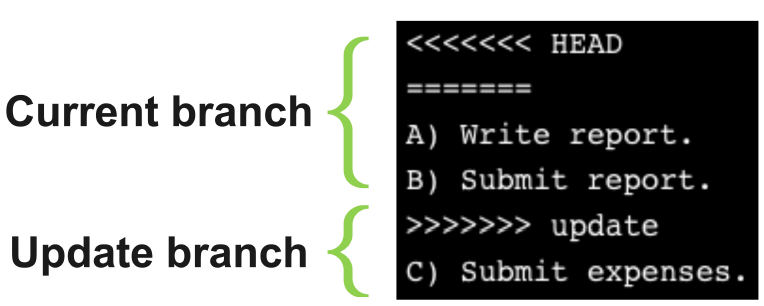
Resolving a conflict
git pull remote_name local_branch
Git will automatically open the nano text editor and ask us to add a message for the merge
Leave a message that we are pulling the latest report from the remote